.jpg)
.jpg)
Net present value (NPV) is a technique used in capital budgeting to find out whether a project will add value or not. It involves finding future cash flows of an option and discounting them to find their present worth and comparing it to the initial outlay required. Another example of how salvage value is used when considering depreciation is when a company goes up for sale. The buyer will want to pay the lowest possible price for the company and will claim higher depreciation of the seller’s assets than the seller would.
Straight-Line Depreciation
You must subtract the asset’s accumulated depreciation expense from the basis cost. Otherwise, you’d be “double-dipping” on your tax deductions, according to the IRS. The estimated salvage value is deducted from the cost of the asset to determine the total depreciable amount of an asset. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires companies to estimate a “reasonable” salvage value. The value depends on how long the company expects to use the asset and how hard the asset is used.
Depreciation Method
For example, if a construction company can sell an inoperable crane for parts at a price of $5,000, that is the crane’s salvage value. If the same crane initially cost the company $50,000, then the total amount depreciated over its useful life is $45,000. Accountants use several methods to depreciate assets, including the straight-line basis, declining balance method, and units of production method.
Strategic Decision Making
If the residual value assumption is set as zero, then the depreciation expense each year will be higher, and the tax benefits from depreciation will be fully maximized. The difference between the asset purchase price and the salvage (residual) value is the total depreciable amount. Starting from the original cost of purchase, we must deduct the product of the annual depreciation expense and the number of years. The Salvage Value is the residual value of a fixed asset at the end of its useful life assumption, after accounting for total depreciation. Companies consider the matching principle when they guess how much an item will lose value and what it might still be worth (salvage value).
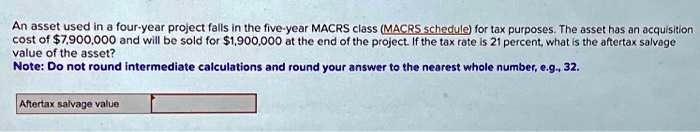
How to Calculate After Tax Salvage Value
- So, salvage value is the money a company expects to make when they get rid of something, even if it doesn’t include all the selling or throwing away costs.
- It’s the expected residual value of the asset after accounting for aspects like depreciation, age-related wear and tear, and obsolescence.
- Depreciation is an essential measurement because it is frequently tax-deductible.
- In other contexts, residual value is the value of the asset at the end of its life less costs to dispose of the asset.
- This value is determined by various factors such as the condition of the asset, market demand, and technological advancements.
It is calculated by subtracting accumulated depreciation from the asset’s original cost. Regardless of the method used, the first step to calculating depreciation is subtracting an asset’s salvage value from its initial cost. Salvage value is the amount for which the asset can be sold at the end of its useful life.
It’s important to note that this method assumes a linear depreciation pattern and may not accurately capture potential asset value variations. Calculating depreciation with consideration of the salvage value ensures that the asset’s cost is accurately spread over its useful life. This provides a true reflection of the asset’s value and helps in presenting a more accurate financial position of the company. It is is an essential component of financial accounting, allowing businesses to allocate the cost of an asset over its useful life. One method of determining depreciation involves considering the asset’s salvage value.

It must be noted that the cost of the asset is recorded on the company’s balance sheet whereas the depreciation amount is recorded in the income statement. Some methods make the item lose more value at the start (accelerated methods), like declining balance, double-declining balance, and sum-of-the-years-digits. The depreciable amount is like the total loss of open an ira and make a contribution before tax day value after all the loss has been recorded. Depreciation, on the other hand, is the systematic allocation of the cost of an asset over its useful life. It is a method of recognizing the decline in value and the wear and tear of an asset over time. Depreciation expense is reported on the income statement and reduces the value of the asset on the balance sheet.
Imagine you are an employee of a mid-sized company tasked with evaluating the financial viability of a major equipment upgrade. The current machinery, after years of service, is approaching the end of its useful life. You’re faced with the decision of whether to sell it or keep it until it becomes obsolete. To make an informed choice, you need to calculate the after-tax salvage value of the equipment, which will significantly impact your company’s financial statements and tax liabilities.
